Exploring the Benefits and Limitations of Deep Drawn Stamping for Sheet Metal Manufacturing
Sheet metal, typically aluminum, steel, or copper, can be used to manufacture complex, hollow parts by deep drawn stamping. In the stamping process, flat sheets of metal are pressed into three-dimensional shapes, such as cylinders and boxes, by drawing them into a die with a stamping press. A punch is used to apply pressure to the sheet metal, causing it to flow into the die cavity, taking on the desired shape as a result.
In addition to producing parts that are highly accurate and consistent, deep drawn stamping have many other advantages. As a result of the process, parts with extremely tight tolerances and uniform wall thicknesses can also be produced, which is particularly important for aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
As well as being efficient and cost-effective, deep drawn stamping has a number of other advantages. By using this process, large quantities of parts can be produced quickly and at a relatively low cost, as compared to casting and forging, for example. Furthermore, deep drawn stamping can be made more efficient and cost-effective by implementing automation and robotics.
The deep drawn stamping method, however, has some limitations. For example, it can only be used to produce simple or symmetrical parts. In order to achieve the desired shape of complex or asymmetrical parts, additional processes such as machining or welding may be required. A deep drawn stamp can also be limited in size and thickness depending on the sheet metal used, with thicker or larger sheets requiring more expensive and complex equipment.
A deep drawn stamping process provides numerous benefits for the production of complex, hollow parts from sheet metal as it is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process. In industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, its accuracy, consistency, and cost-effectiveness make it a popular choice.

What is deep drawn stamping?
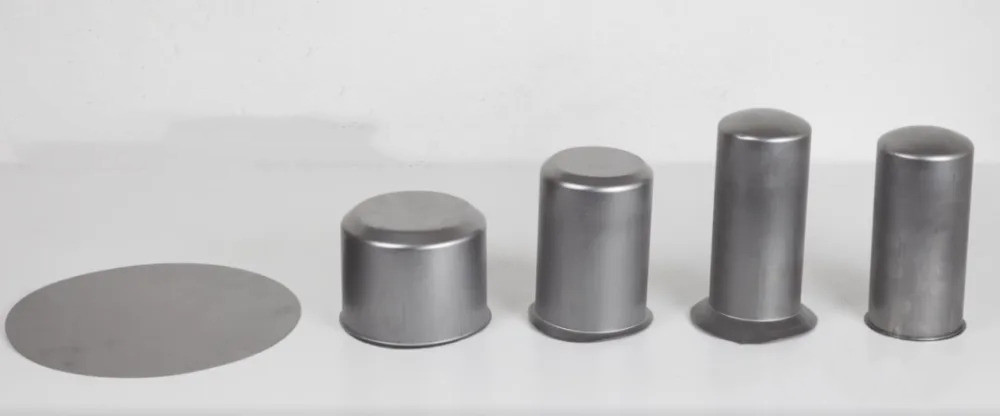
With deep drawn stamping, flat sheet metal can be turned into hollow, three-dimensional objects. Stamping involves applying force to a sheet of metal, which is then dipped into a die cavity to create the desired shape using a stamping press. When applying force to the metal, it flows into the die cavity without fracturing or tearing, which results in a depth of the draw.
A deep drawn stamp can produce complex shapes with precise dimensions and uniform wall thicknesses. It is commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries to create parts such as cans, tubes, and cases. In addition, household appliances, electronics, and other consumer items are also produced using the process.
Its ability to produce parts with high levels of accuracy and consistency, even for complex shapes, is one of its key advantages. By automating the process, large quantities of parts can be produced quickly and efficiently at a relatively low cost, which makes it an excellent choice for mass production.
What types of sheet metal are typically used in deep-drawn stamping?
The deep drawn stamping process involves shaping flat sheets of metal into three-dimensional shapes. A variety of metals can be used in deep drawn stamping, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, brass, and high-strength steel alloys.
The lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties of aluminum make it a popular choice for aerospace and automotive applications. A common use of stainless steel in medical and industrial equipment is its strength and durability. Due to their excellent conductivity, copper and brass are frequently used in electrical and electronic applications.
Depending on the application and desired properties of the final product, deep drawn stamping can use a variety of types of sheet metal. Different grades of steel can be used for parts that require high strength or wear resistance, while softer materials can be used for parts that require flexibility.
Why is deep drawn stamping so effective?
The deep drawn stamping process involves shaping flat sheets of metal into three-dimensional shapes, such as hollow parts such as cylinders and boxes. It involves steps such as blanking, forming, drawing, and trimming.
A sheet of metal is cut into a flat shape, usually a circle or rectangle, in the blanking stage. A blank holder holds the flat sheet in place while it is stamped. The stamping press then applies force to the sheet, causing it to flow into the die cavity and form the desired shape.
During the drawing phase, metal is pulled into a die cavity to create a deep-drawn shape. Metal drawn into the cavity varies based on the die shape and depth, as well as the metal properties.
The finished part is trimmed after the drawing stage, removing any excess metal. The trimming process may be done by hand or by automated equipment.
The deep drawn stamping process requires a combination of pressure, force, and lubrication to achieve the desired shape without tearing or fracturing the metal. A lubricant is used to reduce friction between the metal and the die, as well as to prevent the metal from sticking to the die.
In manufacturing, what are some advantages of deep drawn stamping?
For manufacturers looking to manufacture high-quality metal components, deep drawn stamping offers a number of benefits.
Deep drawn stamping can be automated to produce large quantities of parts quickly and at relatively low cost using highly efficient processes.
Deep drawn stamping produces highly precise and accurate parts with very tight tolerances and uniform wall thicknesses.
The deep drawn stamping process allows complex, three-dimensional shapes to be created that would otherwise be impossible.
It produces highly repeatable and reliable components because it is an automated process that produces parts with consistent quality and dimensions.
Deep drawn stamping can be used with a variety of sheet metal materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and brass, allowing manufacturers to select the best material for their specific need.
Generally speaking, deep drawn stamping offers a range of benefits for quick, efficient, and cost-effective production of high-quality metal components.
What are some industries that commonly use deep drawn stamping?
Metal components are commonly produced using deep drawn stamping, which is a versatile manufacturing process used across several industries.
Engine parts, fuel tanks, and exhaust systems are produced using deep drawn stamping in the automotive industry.
Fuel tanks, wing components, and structural parts are made using deep drawn stamping in the aerospace industry.
Surgical instruments, syringe barrels, and implantable medical devices are all produced using deep drawn stamping.
A wide range of electronic devices are produced using deep drawn stamping, including connectors, terminals, and housings.
Containers such as cans, bottles, and other packaging components are made with deep drawn stamping.
Deep drawn stamping is used for a variety of consumer goods, including cookware, kitchen appliances, and hardware.
The deep drawn stamping process is widely used to produce high-quality metal components for a wide range of applications, and it offers a number of benefits. In many different industries, it is popular due to its versatility and ability to produce precise, complex shapes.

Is it possible to produce complex shapes with deep drawn stamping?
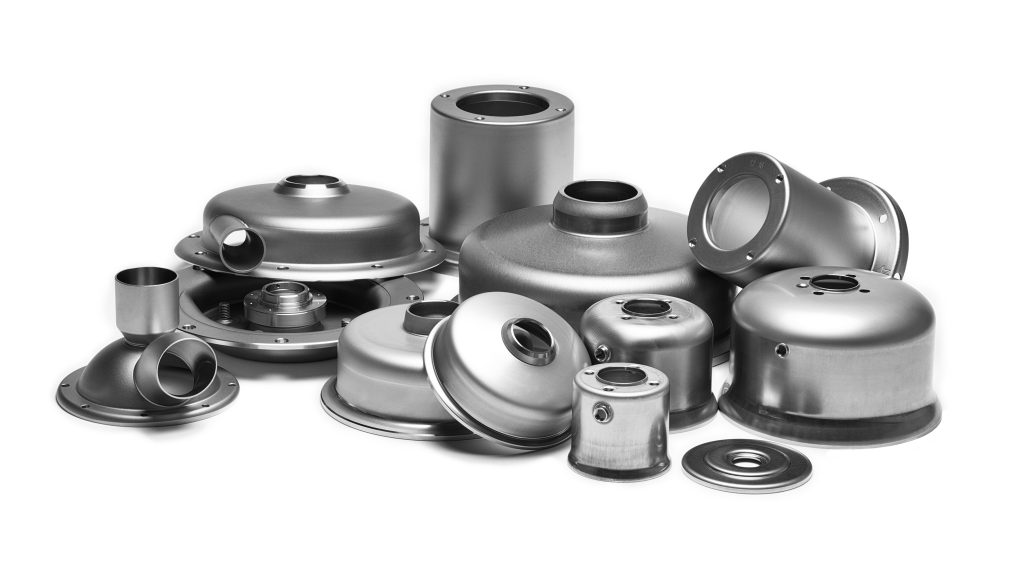
With deep drawn stamping, it is possible to create parts with complex shapes, and one of its main advantages is that this manufacturing method makes it possible to produce three-dimensional shapes that would otherwise be impossible.
Using dies and punches, deep drawn stamping produces complex, three-dimensional shapes from flat sheets of metal. It involves drawing, forming, and tinkering, and can produce parts of specific sizes, shapes, and characteristics.
A wide range of metals can also be used in deep drawn stamping, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and brass, giving manufacturers the ability to produce complex parts with different mechanical properties.
In terms of cost-effectiveness, how does deep drawn stamping compare to other manufacturing methods?
When compared to other manufacturing methods, deep drawn stamping is cost-effective. In this process, flat sheets of metal are shaped into complex, three-dimensional forms using a series of dies and punches, and high-volume production runs can be automated. Manufacturers are able to produce parts more quickly and efficiently, lowering labor costs and increasing productivity as a result.
Furthermore, deep drawn stamping can use a variety of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and brass, which can be purchased in sheet form for a relatively low price. As a result, material waste is reduced and raw materials are better utilized, resulting in additional savings.
This also reduces the need for additional finishing processes, which further reduces production times and costs. Deep drawn stamping produces highly accurate, repeatable parts, also reducing costs.